- Date
- 29 Nov 2019
- Copyright
- © 2019 by the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI), Norrköping, Sweden
- Legals
- baltrad-ppc is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
- baltrad-ppc is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more details.
- You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License along with baltrad-ppc. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/. By obtaining, using, and/or copying this software and/or its associated documentation, you agree that you have read, understood, and will comply with the following terms and conditions:
Introduction
The baltrad polarimetric processing chain quality algorithm is based on the work made by Gianfranco Vulpiani at SMHI in 2017. The original code was developed in Matlab and has been ported to work as a part of RAVE.
This documentation focus on the software and usage of the results so you will have to read the report for a more indepth knowledge about the original implementation and the physics behind it all.
Overview
The processing chain performs several different steps in order to produce an attenuation corrected result and is best described by the following picture.
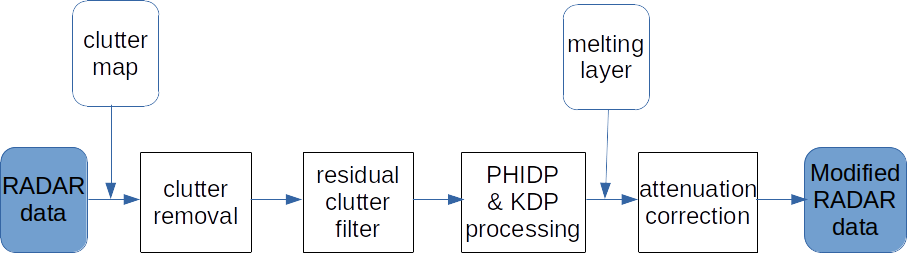
The steps performed in the processing chain are:
- Clutter filtering
- Is based on Fuzzy Logic using the reflectivity factor (Z), doppler velocity (V), the correlation coefficient ρHV, the texture of ΦDP and a statistical clutter map (cmap). The statistical clutter map has to be calculated externally and given to the process function in the _pdpprocessor module described later in this documentation.
- Residual clutter filtering
- Residual, often isolated, clutter pixels can be removed by applying a median filter.
- Processing of differential phase shift and an estimation of the specific differential phase
- The measured differential phase is affected by system noise, backscatter differential phase, system offset and, potentially, by aliasing-related wrapping
- Filtering based on melting layer height
- When generating the attenuation mask, the bin heights must be below the melting layer height before taking RHOHV, KDP and TH into account.
- Attenuation correction
- based on two different methods, linear method and ZPHI.
When the above steps have been performed a number of different products will be added to the original radar data and then returned to the user of the process.
Python functions
Some functions have been added to the public python APIs so that it's possible to run parts of the chain if needed. For example in tests or when evaluating the functions. There are 3 different modules that can be loaded.
- _pdpprocessor
- Actual processing
- _ppcoptions
- Function for loading xml configuration file
- _ppcradaroptions
- Object containing the configuration for one radar
The documentation for each module is obtained with the following command
>>> import module >>> print(module.__doc__)
The documentation for respective module is displayed below..
Python PDP processor
>>> import _pdpprocessor
>>> print(_pdpprocessor.__doc__)
This is the polarimetric processing chain module itself.
The easiest way to get started is to use the process function which combines all functions into a chain but
first you will have to create an instance of the _pdpprocessor which is done by:
>>> import _pdpprocessor
>>> processor = _pdpprocessor.new()
After that you might have to modify the options that are used by the processor and these can be
accessed with:
>>> processor.options....
Next is to process the data in some way. The fastest way to get started is to use the process function
which only takes a rave polar scan as in argument.
>>> from _ppcradaroptions import P_TH_CORR,P_ZPHI_CORR,P_ATT_TH_CORR,P_ATT_DBZH_CORR,P_KDP_CORR
>>> import _raveio
>>> scan = _raveio.open(".../some.scan.h5").object
>>> processor.requestedFields = P_TH_CORR | P_ZPHI_CORR | P_ATT_TH_CORR | P_ATT_DBZH_CORR | P_KDP_CORR
>>> processor.meltingLayerBottomHeight = 1.0 # In KM
>>> newscan = processor.process(scan)
>>> param = newscan.getParameter("KDP_CORR")
The functions are:
scan := process(scan, clutterMap)
Performs the polarimetric processing chain.
- indata
scan - a polar scan
clutterMap - the statistical clutter map. - returns a scan of type PolarScanParam
texture := texture(field)
Creates a texture from the provided data field.
- indata:
field (RaveData2DCore) - An arbitary field
- returns a texture of type RaveData2DCore
degree := trap(field, a, b, s, t)
Trapezoidal function where the field can be any variable and a,b,s,t
identifies the trapezoid coordinates along the x-axis x1 = a-s, x2=a, x3=b, x4=b+t.
- indata:
field (RaveData2DCore) - An arbitary field
a (float) - see above explanation of constant
b (float) - see above explanation of constant
s (float) - see above explanation of constant
t (float) - see above explanation of constant
- returns a RaveData2DCore field representing the membership degree
(Z, Quality, ClutterMask) := clutterCorrection(Z, VRADH, texturePHIDP, RHOHV, textureZ, ClutterMap, nodataZ, nodataVRADH, qualityThreshold)
Clutter correction function.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
VRADH (RaveData2DCore) - Doppler velocity
TexturePHIDP (RaveData2DCore) - Texture of PHIDP
RHOHV (RaveData2DCore) - Correlation coefficient
TextureZ (RaveData2DCore) - Texture of Z
ClutterMap (RaveData2DCore) - Statistical clutter map
nodataZ (float) - Nodata for Z
nodataVRADH (float) - Nodata for VRADH
qualityThreshold (float) - Threshold for the quality as generated.
- returns a tuple (Z, Quality, ClutterMask) of type RaveData2DCore
degree := clutterID(Z, VRADH, texturePHIDP, RHOHV, TextureZ, ClutterMap, nodataZ, nodataVRADH)
Clutter identification function. That calculates a field containing a degree of membership of a target weather class.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
VRADH (RaveData2DCore) - Doppler velocity
texturePHIDP (PyRaveData2D) - The PHIDP texture RHOHV (RaveData2DCore) - Correlation coefficient
TextureZ (RaveData2DCore) - Texture of Z
ClutterMap (RaveData2DCore) - Statistical clutter map
nodataZ (float) - Nodata for Z
nodataVRADH (float) - Nodata for VRADH
- returns a RaveData2DCore representing probability (degree) of weather class
mask := medfilt(Z, threshZ, nodataZ, (filtXsize, filtYsize))
Median filter. threshZ, nodataZ, filtXsize and filtYsize are optional. filtXsize & filtYsize are specified as a tuple.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
threshZ (float) - Z threshold
nodataZ (float) - Z nodata value
(filtXsize, filtYsize) (2*digit), - window size
- returns a RaveData2DCore field with the mask calculated by the filter
mask := residualClutterFilter(Z, threshZ, threshTexture, (filtXsize, filtYsize))
Residual clutter filter. Z is a RaveData2DCore field. threshZ, threshTexture are doubles and filtXsize, filtYsize are digits. All attributes are optional except Z.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
threshZ (float) - Z threshold
threshTexture (float) - Texture threshold
(filtXsize, filtYsize) (2*digit), - window size
- returns a RaveData2DCore field with the mask calculated by the filter
(PHIDP, KDP) := pdpProcessing(PDP, res, window, nrIter)
this function applies the Iterative Finite Difference scheme for the filtering of PHIDP and estimation of KDP
- indata:
PDP (RaveData2DCore) - Input differential phase to be processed
res (float) - Radial resolution in km
window (number) - Half of moving window size expressed in bins applied to the azimuthal rays.
nrIter (number) - Number of iteration the procedure has to be applied to keep the excpected std dev of KDP under control
- returns a tuple (PHIDP, KDP) of type RaveData2DCore
(PHIDP, KDP) := pdpScript(PDP, dr, rWin1, &rWin2, nrIter)
this function applies the Iterative Finite Difference scheme for the filtering of PHIDP and estimation of KDP
- indata:
PDP (RaveData2DCore) - Input differential phase to be processed
dr (float) - Radial resolution in km
rWin1 (float) - Half of moving window size expressed in km applied to the az-rays
characterized by low to moderate total phase shift
rWin2 (float) - Half of moving window size expressed in km applied to the az-rays
characterized by moderate to high total phase shift
nrIter (number) - Number of iteration the procedure has to be applied to keep the excpected
std dev of KDP under control
- returns a tuple (PHIDP, KDP) of type RaveData2DCore
(Z, ZDR, PIA, DBZH) := attenuation(Z, ZDR, DBZH, PDP, mask, gamma_h, alpha, zundetect, dbzhundetect)
This function applies the linear attenuation.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
ZDR (RaveData2DCore) - Differential reflectivity
DBZH (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
PDP (RaveData2DCore) - Filtered phase shift
mask (RaveData2DCore) - Specifies the first and last range gates in rain to be considered for attenuation
correction see source code for process for more information of type RaveData2DCore
gamma_h (float) - Coefficient relating specific attenuation and specific differential phase.
alpha (float) - Is the quota AH / ADP where AH is the specific attenuation and ADP is the specific differential attenuation.
zundectect (float) - Z fields undetect value.
dbzhundetect (float) - DBZH fields undetect value.
- returns a tuple of attenuated fields (Z, ZDR, PIA, DBZH) of type RaveData2DCore
(Zphi, AH) := zphi(Z, PDP, mask, dr, BB, gamma_h)
This function applies the attenuation correction based on application of the analytical solution of differential equation.
- indata:
Z (RaveData2DCore) - Reflectivity
PDP (RaveData2DCore) - Filtered phase shift
mask (RaveData2DCore) - Specifies the first and last range gates in rain to be considered for attenuation
correction see source code for process for more information
dr (double) - Range resolution expressed in km.
BB (double) - The exponent of the power law relating specific attenuation and Z.
- returns a tuple of attenuated fields (Zphi, AH) of type RaveData2DCore where Zphi is attenuation
corrected reflectivity and AH is estimated specific attenuationPython PPC options class
>>> import _ppcoptions
>>> print(_ppcoptions.__doc__)
This is the ppc options loader. It is used to load ppc radar option configuration files written in xml-format.
There are only a few member functions available here (getRadarOptions, exists and options) and currently there is no support for saving the configuration.
The available functions are:
- radaroptions := getRadarOptions(string)
returns a PpcRadarOptionsCore instance if found
- boolean := exists(string)
returns if the specified option name exists or not
- dictionary := options()
returns a dictionary with all available option settings
>>> import _ppcoptions
>>> options = _ppcoptions.load(".../ppc_options.xml")
>>> optionNames = options.options().keys()
>>> print(optionNames)
dict_keys(['default'])
Assuming that we are loading a polar scan from sehud and want to use the options configured for that site
one could implement the usage as follows:
>>> sehudopt = options.getRadarOptions("default")
>>> if options.exists("sehud"):
>>> sehudopt = options.getRadarOptions("sehud")
....
Python PPC radar options class
>>> import _ppcradaroptions
>>> print(_ppcradaroptions.__doc__)
Keeps track of options used for the different radar sources when it comes to the polarimetric process chain
processing. In this documentation section all the available options are listed for the different radars and a description of the values they assume.
The following settings are available:
parametersUZ - parameters for TH, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
parametersVEL - parameters for VRADH, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
parametersTextPHIDP - parameters for the PHIDP texture, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
parametersRHV - parameters for RHOHV, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
parametersTextUZ - parameters for the TH texture, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
parametersClutterMap - parameters for the clutter map, 5 values separated by ',' Weight,X2,X3,Delta1,Delta2
and the derived values will be X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2
nodata - nodata to be used in most products
minDBZ - min DBZ threshold in the clutter correction
qualityThreshold - quality threshold in the clutter correction
preprocessZThreshold - preprocessing Z threshold before starting actual processing
residualMinZClutterThreshold - min z clutter threshold during residual clutter filtering
residualThresholdZ - min Z threshold in the residual clutter filtering
residualThresholdTexture - texture threshold in the residual clutter filtering
residualClutterNodata - the nodata value to be used when creating the residual clutter image used for creating the mask
residualClutterMaskNodata - Nodata value for the residual clutter mask
residualClutterTextureFilteringMaxZ - Max Z value when creating the residual clutter mask, anything higher will be set to min value
residualFilterBinSize - number of bins used in the window when creating the residual mask
residualFilterRaySize - number of rays used in the window when creating the residual mask
minZMedfilterThreshold - min z threshold used in the median filter that is used by the residual clutter filter
processingTextureThreshold - threshold for the texture created in the pdp processing
minWindow - min window size
pdpRWin1 - pdp ray window 1
pdpRWin2 - pdp ray window 2
pdpNrIterations - number of iterations in pdp processing
kdpUp - Maximum allowed value of Kdp
kdpDown - Minimum allowed value of kdp
kdpStdThreshold - Kdp STD threshold
BB - BB value used in the zphi part of the pdp processing
thresholdPhidp - threshold for PHIDP in the pdp processing
minAttenuationMaskRHOHV - min RHOHV value for marking value as 1 in the attenuation mask
minAttenuationMaskKDP - min KDP value for marking value as 1 in the attenuation mask
minAttenuationMaskTH - min TH value for marking value as 1 in the attenuation mask
attenuationGammaH - gamma h value used in the attenuation
attenuationAlpha - alpha value used in the attenuation
attenuationPIAminZ - min PIA Z value in attenuation process
meltingLayerBottomHeight - The melting layer bottom height
meltingLayerHourThreshold - The number of hours before default height should be used.
invertPHIDP - if the PHIDP should be inverted (multiplied with -1) or not. Typically this can be needed if the RSP produces inverted values.
requestedFields - '|' separated list of flags that defines what products should be added to the finished result.
If the flag begins with a P, it means that the result is added as a parameter and the name of
the parameter will be without the P_. If on the other hand the flag begins with a Q_ it means
that the result is added as a quality field and in those cases the how/task name will be
se.baltrad.ppc.<mask name without Q_ in lowercase>
Available flags are:
+ P_TH_CORR
+ P_ATT_TH_CORR
+ P_DBZH_CORR
+ P_ATT_DBZH_CORR
+ P_KDP_CORR
+ P_RHOHV_CORR
+ P_PHIDP_CORR
+ P_ZDR_CORR
+ P_ZPHI_CORR
+ Q_RESIDUAL_CLUTTER_MASK
+ Q_ATTENUATION_MASK
+ Q_ATTENUATION
Rave PGF plugin
It is probably the rave plugin that will be used the most. The actual registration of the plugin is performed in the same way as other plugins are registered in rave. Either the file .../rave_pgf_quality_registry.xml file is modified manually or else a small python script containing the following is written.
from rave_pgf_quality_registry_mgr import rave_pgf_quality_registry_mgr
a = rave_pgf_quality_registry_mgr("/etc/baltrad/rave/etc/rave_pgf_quality_registry.xml")
a.remove_plugin("ppc")
a.add_plugin("ppc", "ppc_quality_plugin", "ppc_quality_plugin")
a.save("/etc/baltrad/rave/etc/rave_pgf_quality_registry.xml")
ppc_options.xml
Next step is to configure the various settings for respective radar. This file /etc/baltrad/baltrad-ppc/config/ppc_options.xml is used to configure the various options for the different radars. In ppc_options.xml you will find a brief explanation of the different parameters that are configurable and also how you can reuse configuration for different radar sources.
The information described in the xml file will be roughly the same as explained when printing the doc for _ppcradaroptions. Some things to note though is that it is possible to build hierarchies of the properties. This means that you can differentiate configurations depending on the situation. To get this configuration you will be able to override configuration settings from a parent. This is achieved by inheriting the options by defining a default attribute in the radaroptions-tag.
As an example, let us say that seang & sekkr should use default values except for attenuationAlpha. selul should use the same attenuationAlpha as sekkr but it also needs to different attenuationGammaH set to 0.09. First you define an option group with the name default (<radaroptions name="default">). After that you define a subgroup called attenuationAlpha03 inheriting default setting from the previously created group. sekkr will just inherit attenuationAlpha03s options and selul will inherit sekkr with the modified attenuationGammaH. Obviously, it's possible to setup these options in several different ways all depending on needs.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<ppc-options>
<radaroptions name="default">
<!-- Weight | X2 | X3 | Delta1 | Delta2 X1=X2-Delta1, X3=X4-Delta2-->
<parametersUZ value="0.00,30.00,90.00,62.00,20.00" />
<parametersVEL value="0.30,-0.90,0.90,0.15,0.15" />
<parametersTextPHIDP value="0.80,15.00,40.00,5.00,40.00" />
<parametersRHV value="0.20,0.00,0.60,0.00,0.10" />
<parametersTextUZ value="0.30,20.00,60.00,5.00,10.00" />
<parametersClutterMap value="0.90,5.00,70.00,20.00,60.00" />
<minWindow value="11" />
<nodata value="-999.0" />
<minDBZ value="-32.0" />
<qualityThreshold value="0.75" />
<preprocessZThreshold value="-20.0" />
<residualMinZClutterThreshold value="-31.5" />
<residualThresholdZ value="-20.0" />
<residualThresholdTexture value="20.0" />
<residualClutterNodata value="-999.0" />
<residualClutterMaskNodata value="-1.0" />
<residualClutterTextureFilteringMaxZ value="70.0" />
<residualClutterNodata value="-31.5" />
<residualFilterBinSize value="1" />
<residualFilterRaySize value="1" />
<minZMedfilterThreshold value="-30.0" />
<processingTextureThreshold value="10.0" />
<pdpRWin1 value="3.5" />
<pdpRWin2 value="1.5" />
<pdpNrIterations value="2" />
<kdpUp value="20.0" />
<kdpDown value="-2.0" />
<kdpStdThreshold value="5.0" />
<BB value="0.7987" />
<thresholdPhidp value="40.0" />
<minAttenuationMaskRHOHV value="0.8" />
<minAttenuationMaskKDP value="0.001" />
<minAttenuationMaskTH value="-20.0" />
<attenuationGammaH value="0.08" />
<attenuationAlpha value="0.2" />
<attenuationPIAminZ value="-30" />
<meltingLayerBottomHeight value="2.463" />
<meltingLayerHourThreshold value="6" />
<invertPHIDP value="0" />
<requestedFields value="P_DBZH_CORR|P_ATT_DBZH_CORR|P_PHIDP_CORR|P_QUALITY_RESIDUAL_CLUTTER_MASK" />
</radaroptions>
<radaroptions name="attenuationAlpha03" default="default" > <!-- Uses default above but with some modified values-->
<attenuationAlpha value="0.3" />
</radaroptions>
<radaroptions name="seang" default="attenuationAlpha03" > <!-- Attenuation alpha 0.3 -->
</radaroptions>
<radaroptions name="sekkr" default="attenuationAlpha03" > <!-- Attenuation alpha 0.3 -->
</radaroptions>
<radaroptions name="selul" default="sekkr" > <!-- Attenuation alpha 0.3 & attenuationGammaH 0.09 -->
<attenuationGammaH value="0.09" />
</radaroptions>
</ppc-options>
Generated by