BALTRAD
2. Basic description
a) Physical basis of the algorithm
The vertical profile of radar reflectivity factor (VPR) and the measurement geometry of weather radar introduce a vertical sampling difference between the actual precipitation at ground level and the radar estimate of it. VPR correction is used to modify the measured values so that they represent the precipitation conditions at ground level more accurately. The networked VPR correction described here denotes that the correction is calculated in radar networks so that the adjustment factor field will be continuous, not introducing additional steps at the seam lines where measured data from neighboring radars meet.
b) Amount of validation performed so far
Algorithm is implemented and used operationally at FMI since the year 2004. Validation has been performed applying gauge-radar and radar-radar comparisons.
c) References (names and contact information of all developers during the evolutionary history, scientific papers)
Operational estimation of ground level reflectivity in radar networks applying ensembles of VPR corrections. Jarmo Koistinen and Heikki Pohjola Article isn’t published yet.
3. ODIM metadata requirements for I/O
/dataset/what: gain, offset, nodata
4. Input data
a) What kind of radar data (including the list of previous algorithms and quality flags applied)
Full volume scan reflectivity data(for each radar). At FMI the VPR correction for a 500 m PseudoCAPPI composite is performed presently applying the 4 lowest elevation angles from each radar. Other number of elevations can be applied according to the user selections.
b) Other data (optional and mandatory, applying “universally” agreed formats, geometry)
The classification scheme of VPRs embedded into the correction algorithm and used in real time requires that the height of the freezing level is known at each radar site at each volume scan moment. At FMI that is estimated from NWP nowcasting data applying the HIRLAM model fields of temperature.
5. Logical steps
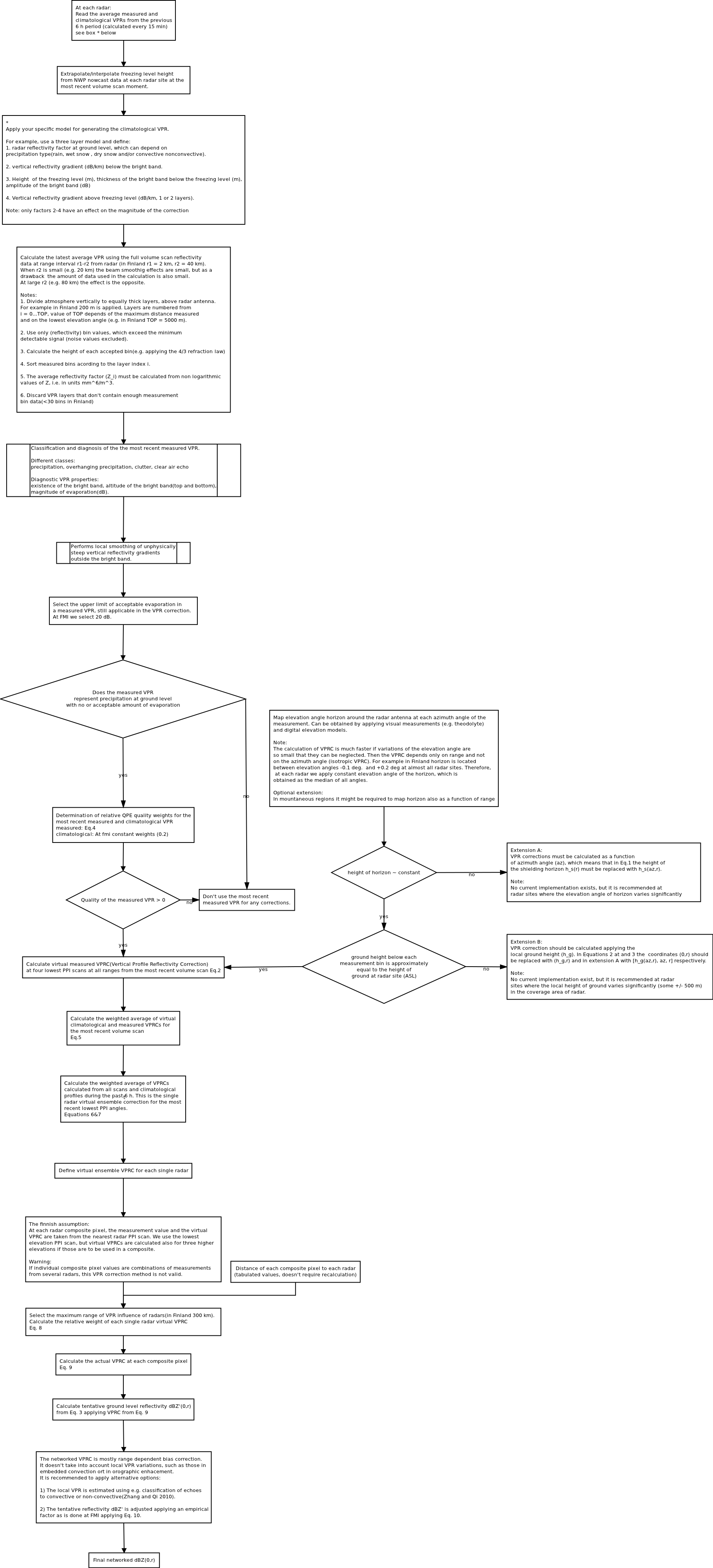
Equations
