BALTRAD
1. Algorithm name
Quality-based PPI (Plan Position Indicator) product generation – Product2D: PPI
2. Basic description
a) Physical basis of the algorithm
The algorithm interpolates polar data into Cartesian coordinates employing quality information (quality index e.g. from QI_TOTAL processing). It can be applied e.g. to radar reflectivity Z after VPR-based extrapolation down to ground.
The product is the basis for generating other 2-D products.
b) Amount of validation performed so far
Not performed yet.
c) References (names and contact information of all developers during the evolutionary history, scientific papers)
IMGW, Department of Ground Based Remote Sensing.
3. ODIM metadata requirements for I/O
Input data: SCAN
- General “what”: source(NOD).
- Dataset-specific “where” for data and QI: nbins, nrays.
- Data-specific “what” for data: gain, offset, nodata, undetect.
- Data-specific “what” for QI: gain, offset, nodata, undetect.
Output data: Cartesian data
- Top-level “where”: lon, lat, xsize, ysize, xscale, yscale.
- Dataset-specific “what”: product.
- Data-specific “what” for data: gain, offset, nodata, undetect.
- Data-specific “what” for QI: gain, offset, nodata, undetect.
4. Input data
a) What kind of radar data (including the list of previous algorithms and quality flags applied)
- Radar-based quantity, e.g. reflectivity data after corrections DBZH as SCAN object.
- Optionally QI information QIND (generated e.g. by QI_TOTAL algorithm) included in the same SCAN object.
b) Other data (optional and mandatory, applying “universally” agreed formats, geometry)
Defined projection and domain of Cartesian output.
5. Logical steps, using any of: text, flow charts, graphics, equations (or references to equations), conditional branches in “all possible cases”.
The algorithm transforms values for measurement gates of polar coordinates (α’’, ‘‘l’’), where ‘‘α’’ is the azimuth, ‘‘l’’ is the distance from the radar site, into values interpolated for Cartesian pixels defined by coordinates: (‘‘x’’, ‘‘y).
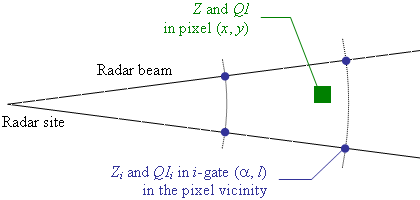
Fig. 1. Scheme of interpolation of gate values into Cartesian pixel.
Algorithm parameters
Set of the algorithm parameters:
| Description | Denotation | Available options | Default value |
| Interpolation method | Method | nearest / uniform / inverse1 / inverse2 / bilinear / cressman | bilinear |
| Input quantity identifier | Quantity | TH / DBZH / … | DBZH |
| If to employ quality information QI for interpolation | IncludeQuality | 0 (no) / 1 (yes) | 1 |
| Input quality field name | QIField | pl.imgw.qi_total / se.smhi.detector.poo / … | pl.imgw.qi_total |
| If to interpolate values in mm^6^ m^-3^ (for Quantity = TH / TV/ DBZH / DBZV / ZDR) | dBZtoZ | 0 (no) / 1 (yes) | 1 |
Separation of pixels due to distance to radar
The algorithm interpolates data in different ways for pixels close to radar site, where there is dense pattern of gates, and farther from radar site (so called inside and outside method). The border in distance to radar (D’’) is defined by empirically determined function of measurement parameters: step in azimuth d’‘Az’’ (°), step in distance from radar d’‘bin (km), and Cartesian spatial resolution dx (km):
For instance, for d_Az’’ 1 km, and d’‘x_ 57,5 km.
Inside method
For the centre of Cartesian pixel its four corners are considered, which coordinates are transformed into polar coordinates defining investigation area in polar data. Then the number of gates inside this area is determined. If it is higher than 2 the inside method based on quality weighted interpolation is employed:
where n is the number of gates inside the investigation area.
Otherwise (if the number of gates inside the investigation area is not higher than 2) the outside method is applied.
Outside method
In outside method the closest gates are determined in the following way. The coordinates of the Cartesian pixel centre are transformed into polar coordinates and four surrounding gates are taken into account. In case when difference between the considered pixel centre and one or two the investigated gates is lower than the preset limit (5% of “rscale” or azimuth step in terms of distance to radar or azimuth respectively) then only the closest gates are taken into calculations.
Then quantity in given pixel of coordinates (x’’, ‘‘y’’) is estimated as weighing average value ‘‘Z’’(‘‘x’’, ‘‘y’’) from the ‘‘n’’ selected gates ‘‘Zi, taking both distances to the gates and data quality information in the gates into account:
where: WDi’’ is the weight related to distance of ‘‘i’‘-gate to pixel (‘‘x’’, ‘‘y’’); ‘‘WQIi’’ is the quality index ‘‘QI’’ of the ‘‘i’‘-gate; ‘‘n is the number of the closest gates taken into account.
Determination of weigths in outside method
The polar coordinates of selected i’‘-gate are transformed into Cartesian coordinates (‘‘x,,i,,’’, ‘‘y,,i,,’’) in order to determine its distance to the considered pixel (‘‘x’’, ‘‘y):
Weights due to distances to gates Di are determined by means of the following methods:
- nearest:
- uniform:
- inverse1:
- inverse2:
- bilinear:
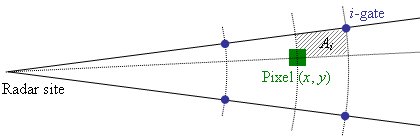
Fig. 2. Scheme of bilinerar interpolation.
where Ai is the area of annulus sector.
- cressman:
where a’’ is the influence radius, ‘‘a 0. If for the considered pixel there are no gates with Di’’ < ‘‘a’’ then the calculation is repeated with longer ‘‘a = 20 km.
Weights due to data quality for 1, .., n pixels are determined as:
Data quality characterization
Quality index for interpolated pixel (x’’, ‘‘y) is calculated in dependence on method applied to data interpolation:
- for inside method
- for outside method
where: WDi’’ are the distance-related weights for ‘‘n selected gates.
6. Output
a) Data type using ODIM notation where possible, e.g. DBZH
- Input quantity as IMAGE or COMP objects (in Cartesian coordinates) with
- “pl.imgw.product2d.ppi” in quality-specific “how”: task,
- interpolation method, selected quality field name, and whether values were interpolated in mm^6^ m^-3^, listed in “how”: task_args.
b) Quality index (QI) field
- Quality index field QIND as IMAGE or COMP objects with:
- “pl.imgw.product2d.ppi” in quality-specific “how”: task,
- interpolation method and selected quality field name listed in “how”: task_args.
7. Outline of a test concept exemplifying the algorithm, as a suggestion for checking that an implementation has been successful.
TBD